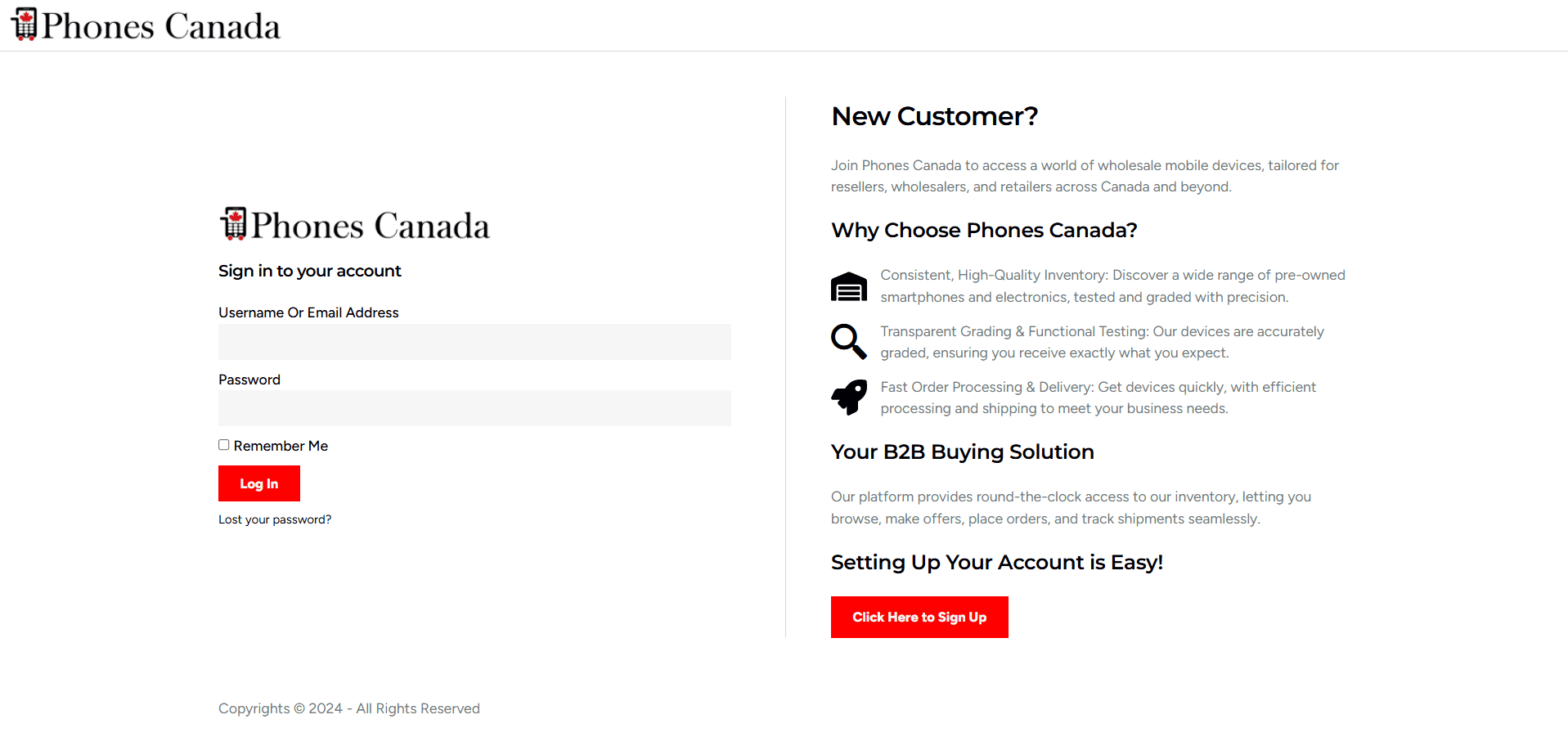
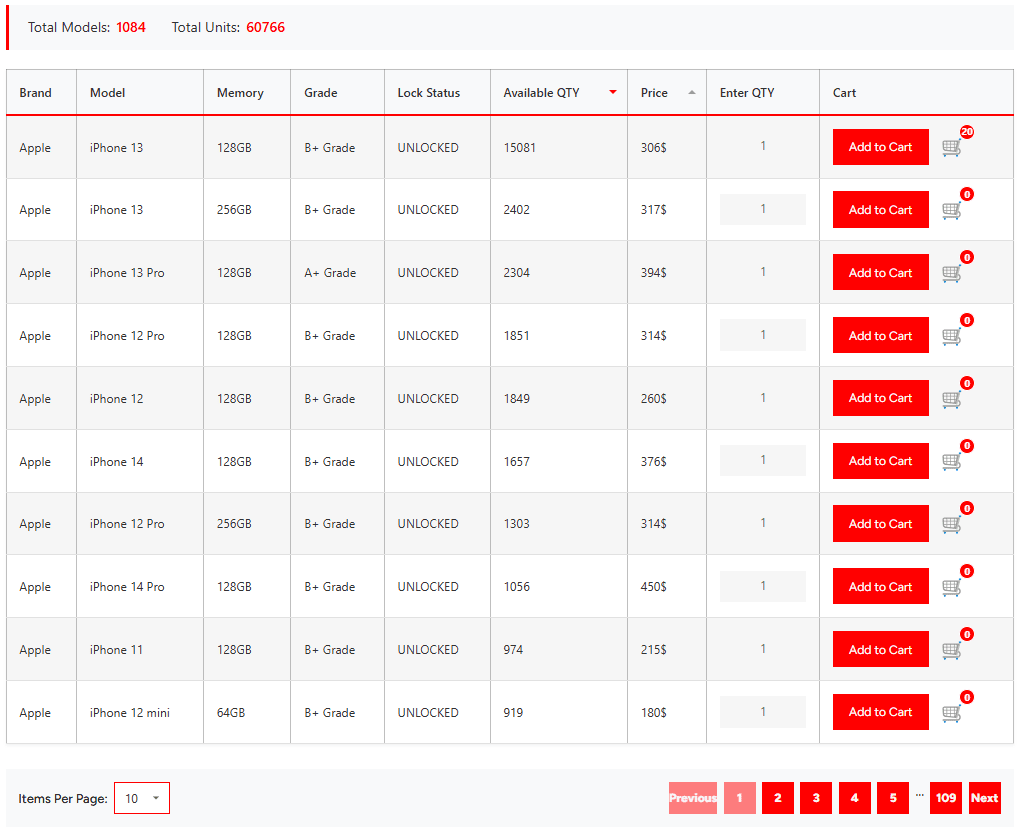
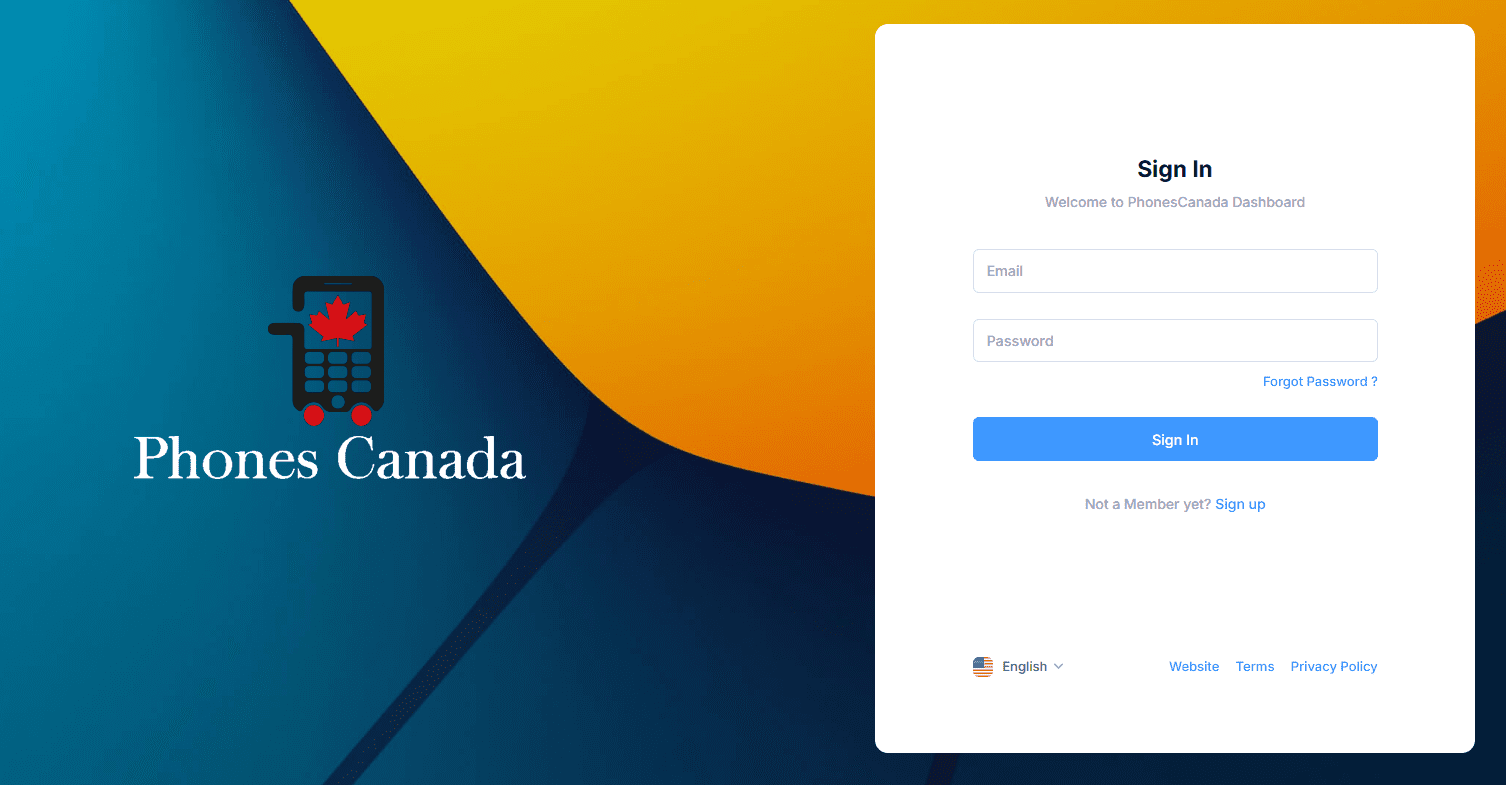
Buying a smartphone used to be simple, but now it’s become more complex. Today, to make an informed decision, you need to understand technical details like the application processor (AP), the foundry that produced the chip, the process node used, and the number of transistors in the chipset. And these are just a few of the factors to consider.
The cameras, sensors, modems, storage, memory, and battery are all important too. Knowing these details can make the difference between buying a phone that suits your needs and one that doesn’t. Do you need a powerful phone, extended battery life, top-notch cameras, or advanced AI features?
For instance, the transistor count of mobile chips has grown significantly from the 20nm A8 bionic in 2018 to the current 3nm A17 Pro, increasing from 4.3 billion to 19 billion transistors.
TSMC recently announced that its 1.4nm node will follow the 2nm node. The smaller the node, the more powerful and energy-efficient a chip can be. A14, the 1.4nm process node, will use Gate-All-Around (GAA) transistors, allowing for more powerful chips with reduced power consumption. While it’s projected to start high-volume manufacturing between 2027 and 2028, there could always be unexpected delays.
Continuing to create smaller, faster, and more energy-efficient components is among the most challenging tasks in the world. The journey to further innovation continues.